PSA finds those proteins which contain a given amino acid sequence. [ Hide ]
Drag some building blocks to Your sequence to build a query. A place can contain multiple amino acids. You can use wildcards (? *).
Scroll down for more help and terms of use.
Manual
Simple version
- The colorful building blocks correspond to amino acids and wildcards.
- Color code:
Small nonpolar,
Negatively charged,
Hydrophobic,
Positively charged,
Polar.
This color code comes from the book Lesk, Introduction to Bioinformatics.
- Color code:
Small nonpolar,
Negatively charged,
Hydrophobic,
Positively charged,
Polar.
- The editing area is found under Your sequence and consists of slots.
- Each slot can accomodate either a wildcard (? or *), or one or more amino acids.
- ? means any amino acid.
- * means any amino acids (zero or more).
- You can
- create a new slot by dragging a building block here:

- add a block to an existing slot by dragging it into the slot
- Wildcards replace everything already in the slot.
- remove a block from the editing area by simply clicking it
- rearrange slots by grabbing them by the blue handle and dragging them around
- discard the current query and start a new one by clicking

- create a new slot by dragging a building block here:
- Click
 to start the search.
to start the search. - An example query:
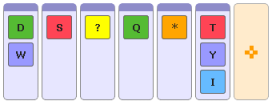
Advanced version (regular expressions)
- This section is intended mainly for programmers.
- Regular expressions (regex for short) are powerful tools for searching complicated patterns.
- PSA allows not only building a query in a graphical way, but advanced users can input a regex which will be matched against the sequence database.
- As an example, the regex [AY]{5,} matches all proteins which have at least 5 consecutive A or Y. For example, the amino acid sequence DGYAYYAT is matched by this regex.
- More information on regular expressions → here.
Terms of use
You can use this service only if you accept
the following terms: We do not guarantee anything about this
service: We do not state anything about the usability of this
service, and we do not state that the results that we may return
can be used for any purpose. We cannot guarantee that this
service will be available in the future, and we cannot guarantee
that your query would generate any output at all.
Privacy: We will not give out your
data to anyone, and, regularly, only you can retrieve the
results to your query using the unique webpage identifier
generated for you. However, we cannot guarantee that others do
not intercept the traffic between you and our server.
Therefore, do not use our webserver for proprietary data
analysis, we cannot guarantee the data integrity and safety
for you.
How to cite: Daniel Banky, Balazs Szalkai, Vince Grolmusz: An Intuitive Graphical Webserver for Multiple-Choice Protein Sequence Search; Gene, Vol. 539, No. 1, pp. 152-153, April 2014 (also in arXiv:1312.4660)